Classical Mechanics, a cornerstone of physics, is the branch that studies the motion of objects and the forces acting upon them. At the heart of this discipline lies Sir Isaac Newton’s groundbreaking work, encapsulated in his three laws of motion. For NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) students aspiring to embark on a journey into the world of medical and dental sciences, understanding Classical Mechanics and Newton’s Laws is essential. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental concepts of Classical Mechanics and decipher Newton’s Laws in a manner that is both accessible and comprehensive.
The Foundation of Classical Mechanics:
Classical Mechanics, developed in the 17th century, forms the basis for understanding the motion of everyday objects. This branch of physics deals with macroscopic bodies moving at speeds much slower than the speed of light. Classical Mechanics is divided into two main components: kinematics and dynamics.
Read Also : Understanding Circular Motion and Centrifugal Force: The Laws of Motion Demystified
Kinematics
Kinematics focuses on describing the motion of objects without considering the forces responsible for the motion. Key parameters include displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Displacement measures the change in position of an object, velocity quantifies the rate of change of displacement, and acceleration denotes the rate of change of velocity.
Dynamics
Dynamics, on the other hand, explores the forces causing motion and their effects. This involves understanding how forces influence the motion of an object, leading us to Newton’s Laws of Motion.
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Sir Isaac Newton, a brilliant physicist and mathematician, revolutionized the understanding of motion with his three laws, published in his seminal work “Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica” in 1687. These laws provide the foundation for Classical Mechanics and are crucial for comprehending the behavior of objects in motion.
Newton’s First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)
“An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force.”
The first law introduces the concept of inertia, which is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. In simpler terms, if no external force acts on an object, it will maintain its current state of motion (whether at rest or in motion).
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
“The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass.”
Mathematically expressed as F=ma, where F is the force, m is the mass of the object, and a is its acceleration, this law defines the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. In essence, the greater the force applied to an object, the greater its acceleration, provided its mass remains constant.
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
“For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.”
This law emphasizes that every force exerted on an object is met with an equal force in the opposite direction. It illustrates the interconnectedness of forces in pairs, known as action and reaction forces. Understanding this law is vital for comprehending the nature of interactions between objects.
Real-life Applications:
To make the theoretical concepts more tangible, let’s explore some real-life applications of Classical Mechanics and Newton’s Laws.
Automobile Dynamics
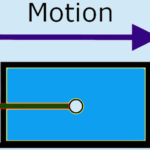
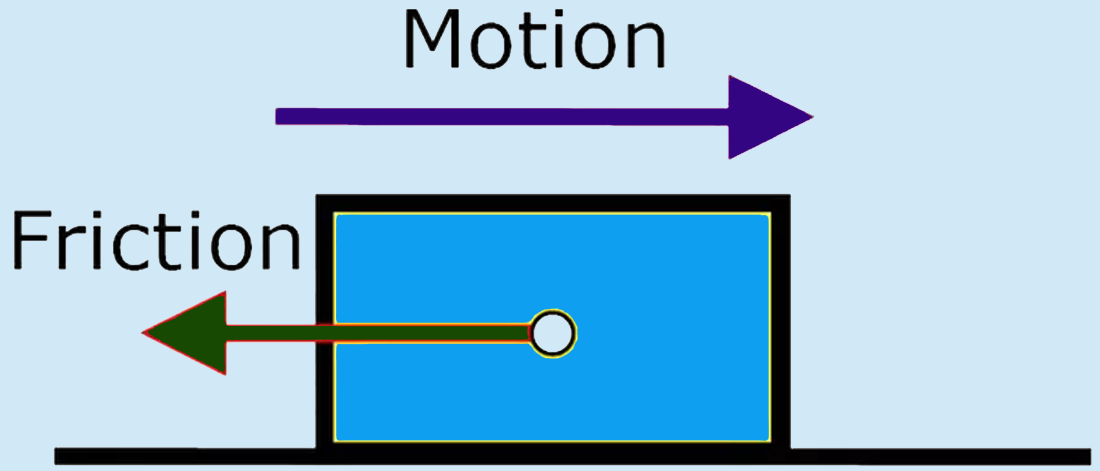
Newton’s laws play a crucial role in understanding the motion of vehicles. When a car accelerates, the force applied by the engine (action) propels the car forward, while the force of friction between the tires and the road (reaction) opposes this motion. Similarly, when a car comes to a stop, the braking force represents an action, with the reaction being the deceleration of the vehicle.
Projectile Motion
The study of projectile motion involves understanding the motion of objects thrown into the air, such as a ball or a projectile. Newton’s laws help predict the trajectory and behavior of these objects, taking into account the force of gravity acting vertically downward and air resistance opposing their motion.
Planetary Motion
Newton’s laws extend beyond Earth to explain the motion of celestial bodies. The gravitational force between the Sun and planets follows Newton’s law of universal gravitation, providing insights into the orbits and movements of heavenly bodies.
Read Also : The Physics of Electricity and Magnetism
Conclusion
In conclusion, Classical Mechanics and Newton’s Laws serve as the bedrock for understanding motion and forces in the physical world. For NEET students aspiring to delve into the intricacies of medical and dental sciences, a solid grasp of these principles is essential. By familiarizing ourselves with the foundational concepts of kinematics and dynamics and delving into Newton’s Laws, we pave the way for a deeper comprehension of the world around us. Whether it’s the trajectory of a projectile or the dynamics of a moving car, the principles of Classical Mechanics are omnipresent, guiding our understanding of the physical universe.